In 2024, the payment and commerce industry saw significant growth, led by the growing usage of eCommerce platforms and a steady demand for payment gateways. FinTech companies were busy improving and perfecting consumer payment options and offering them more convenient ways to pay at the point of sale.
In 2025, merchants must focus on future commerce and payment trends to keep up with the evolving market. Businesses must take essential steps to stay competitive in the fierce market and adapt to innovations shaping the industry in the coming year.
An Overview of Commerce and Payment Trends to watch for in 2025:
1. AI-Driven Transformation in Payment Systems
AI was at the center of every conversation across industries this year – so we will start this list with AI trends in the market. AI, or artificial intelligence, will reshape how payments work in 2025. The key areas where AI can significantly leap this year are security and customer convenience.
Fraud detection will become more prevalent in the market with the help of AI. Earlier businesses that were hesitant to adopt robust fraud detection systems will be more willing to do so, mainly because of the cost efficiency caused by the widespread usage of AI in 2024.
These AI fraud detection systems efficiently monitor real-time transactions to flag suspicious transactions. They are specifically targeted at high-risk areas like cross-border payments. For example, Swift plans to launch an AI-based anomaly detection service in January 2025 to help banks identify and prevent potential financial crimes during international transactions.
Visa has already shown the impact of AI in reducing fraud. In 2023, the company used AI to block 80 million fraudulent transactions, protecting $40 billion globally.
AI also simplifies regulatory compliance by automating processes to ensure that transactions meet local and global rules. This reduces the effort required from businesses to stay compliant. Additionally, payment apps with AI-driven personal finance features offer users real-time, tailored advice to help them manage their money better.
By 2025, AI will improve the security of payment systems and make them more efficient, accessible, and user-focused.
2. Digital Payments will Keep Evolving with Consumer Needs

Innovations in digital payments are progressing quickly, with notable growth across various methods. According to a 2024 report, 92% of U.S. consumers used some form of digital payment in the past year, reflecting a steady rise in adoption. Globally, the digital payments market is expected to grow at an annual rate of 11.79% between 2023 and 2027, with total transactions projected to reach $14.79 trillion by 2027.
Consumer preferences play a major role in shaping digital payment trends. Whether online or brick-and-mortar, businesses can boost sales and improve customer convenience by offering digital payment options. Choosing the right methods requires understanding the specific needs of the target audience.
Tap-to-Pay Usage Increases
Contactless payments, especially tap-to-pay, are becoming more widespread. In the first quarter of 2024, 79% of in-store transactions globally were completed using tap-to-pay, a 5% increase from the last quarter of 2023.
Growth in QR Code Payments
QR code payments are also gaining traction. In 2022, 89 million Americans used their mobile devices to scan QR codes for payments, a 26% rise compared to 2020.
Rise of Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) Services
Buy Now, Pay Later services are extending their reach beyond retail. In 2024, 40% of consumers used BNPL options at least once. Gen Z and millennials are the primary drivers and are attracted to flexible payment terms.
3. Growth and Impact of Payment Orchestration Platforms
Payment orchestration platforms help merchants manage multiple payment processors more effectively, improving transaction success rates with features like smart routing. This functionality redirects failed transactions to alternative processors, increasing approval rates and enhancing overall payment efficiency.
The global market for payment orchestration platforms has grown substantially. Valued at $1.2 billion in 2023, it is expected to reach $6.3 billion by 2032, growing at an annual rate of about 19%.
Several factors drive this growth. The increasing complexity of payment systems requires solutions that streamline operations and efficiently handle multiple payment methods. Features like smart routing improve payment success rates, while integration with options like local payment methods and Buy Now Pay Later services reduces fees and enhances customer satisfaction.
The industry’s shift toward the ISO 20022 standard further supports adopting payment orchestration platforms. This global standard aims to improve interoperability and efficiency in payment processing. Key milestones include the Fedwire Funds Services’ adoption of ISO 20022 messaging formats by March 2025 and the SWIFT network’s full migration by November 2025.
Payment orchestration platforms are well-equipped to align with these developments, enabling merchants to integrate standardized messaging formats and access a wider range of payment options.
4. Unified Apps and Integrated Financial Solutions
“Super apps,” which combine multiple services within a single platform, are becoming more popular outside East Asia, with significant growth expected in North America and Europe by 2025. This rise is fueled by embedded finance, allowing non-financial platforms to integrate services like payments, lending, and insurance, offering users greater convenience and streamlined experiences.
In Western markets, private companies are in charge of creating these comprehensive platforms. For instance, fintech firms like Revolut have expanded their services to include banking, wealth management, cryptocurrency trading, and more, positioning themselves as all-in-one financial apps. Similarly, companies like Klarna, known for Buy Now Pay Later services, are broadening their platforms with features such as price comparisons, cashback offers, and banking capabilities. Trade Republic, a German neobroker, is moving toward a full-service financial platform by introducing salary and bill payment services and applying for a banking license in Spain.
As super apps evolve, embedded finance remains a driving force, allowing seamless integration of financial tools into existing platforms. The convenience of having multiple services in one app aligns with growing consumer expectations for simplified digital experiences. Businesses aiming to enter this space must prioritize user-friendly interfaces, navigate complex financial regulations, and implement strong security measures to protect user data. With increasing demand for integrated solutions, the development of super apps in Western markets is expected to expand rapidly.
5. Rise of Unified Commerce Platforms for Seamless Digital Shopping Experiences

In response to the growing demand for integrated digital shopping experiences, businesses are turning to unified commerce platforms to streamline back-end operations. These platforms consolidate various sales channels, such as physical stores, online shops, mobile apps, and social media, into a single system. This integration allows companies to manage inventory, process payments, fulfill orders, and oversee customer interactions more effectively.
A unified commerce approach provides significant benefits. It enhances the customer experience by delivering consistent and personalized interactions across all channels, meeting modern consumer expectations for connected shopping experiences. Centralizing back-end processes improves operational efficiency by reducing redundancies and increasing data accuracy. Additionally, unifying data enables real-time insights into sales performance and customer behavior, which supports informed decision-making.
6. Impact of Open Banking on Real-Time Payments and A2A Transactions
Open banking, which involves the secure sharing of financial data between banks and authorized third-party providers through APIs, significantly improves the efficiency of real-time payments. By enabling direct account-to-account (A2A) transactions, open banking supports faster payment authorizations and settlements, addressing the increasing demand for speed and transparency in financial transactions.
The global value of open banking transactions is set to rise dramatically, with projections increasing from $57 billion in 2023 to $330 billion by 2027, reflecting widespread adoption. In the UK alone, transaction values are expected to grow from $13.6 billion in 2023 to $82 billion by 2027, showcasing a similar upward trend.
A2A payments are also expanding rapidly. In global e-commerce, these payments are predicted to grow at a CAGR of 14% between 2023 and 2027, solidifying their role as a key payment method. On a broader scale, the volume of A2A transactions worldwide is projected to increase from 60 billion in 2024 to 186 billion by 2029, representing a 209% growth.
The real-time payments market is also experiencing significant growth, with global transaction values forecasted to reach $22 trillion in 2024. The rapid adoption of instant payment solutions highlights the transformative potential of open banking integration, which offers faster, more transparent, and more efficient payment systems to meet the evolving needs of consumers and businesses.
7. Rise of Embedded B2B Payments

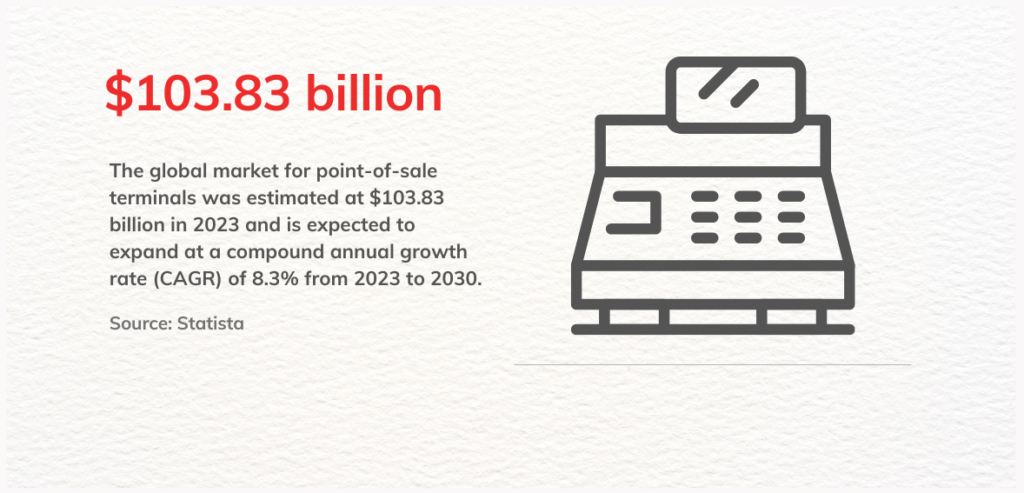
Embedded payments, which have already transformed consumer transactions, are now significantly impacting B2B payments. Companies can enhance payment efficiency, automate billing processes, and improve client interactions by integrating payment processing directly into business platforms. The embedded finance market is witnessing rapid growth. Its global value was estimated at approximately $83.32 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 32.8% from 2024 to 2030.
Specifically, embedded B2B payments are becoming increasingly prominent. Revenue from embedded B2B payments in platforms is expected to rise from $1.9 billion in 2021 to $6.7 billion by 2026. The adoption of embedded payments in B2B transactions offers several advantages. It improves efficiency by automating invoicing and payment reconciliation, reducing errors and saving time. It also enhances the customer experience by offering a unified payment process within the platform, boosting customer satisfaction and loyalty. Additionally, embedded payments create new revenue opportunities by enabling businesses to provide financial services such as lending or subscription billing.
Conclusion
Technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences will shape the payment and commerce landscape in 2025. As businesses adapt to the rise of AI-driven systems, digital payment methods, and embedded financial services, staying ahead of these trends will be key to meeting customer demands and ensuring operational efficiency. The growth of AI in fraud detection, the expansion of digital payment options, and the increasing popularity of Buy Now, Pay Later services highlight the industry’s shift towards greater convenience and flexibility.
Meanwhile, innovations in payment orchestration platforms, super apps, and open banking will redefine how transactions are processed, paving the way for more integrated, secure, and efficient financial ecosystems. As these developments continue to unfold, companies must remain agile, adapting to the changing landscape to stay competitive in a fast-evolving market.