Have you ever considered why brands select specific colors for their logos and advertising? The influence of color is more significant than it might seem. Colors can sway our feelings and perceptions, directly impacting consumer behavior and purchase choices in marketing. An entire discipline, color theory, is dedicated to exploring the effects of color on our emotions, perceptions, and actions.
The choice of colors plays a critical role in shaping how consumers receive a business’s products and services. Companies can harness a crucial edge in design by grasping the significance of colors and their impact on viewers. Let’s explore the fundamentals of color theory in business and marketing and how you can leverage it to your advantage.
What Is Color Psychology?

Color influences the brain’s emotional sensors, capturing attention, eliciting emotions, providing reassurance, evoking nostalgia, and swaying consumer choices. This significance of color psychology extends beyond simple definitions of what each color signifies in marketing and branding.
The foundation of color psychology in marketing lies in people’s emotional responses to color, shaped by their experiences from childhood through adulthood. It details how colors affect human emotions, behaviors, and perceptions, and how different shades can influence moods and reactions.
Leading brands often become synonymous with their signature colors—Coca-Cola uses red, Starbucks uses green, and Facebook and IBM use different shades of blue. These colors are employed so deliberately and consistently that they are instantly recognizable, often before the company’s tagline or logo is noted. Studies show that people form subconscious judgments about a person, environment, or item within the first 90 seconds of exposure, with 62% to 90% of that impression influenced primarily by color.
Brand colors can be used strategically and creatively across social media, enhancing content recognition. In today’s digital age, where visual media circulates rapidly online, leveraging your brand colors can significantly increase your brand’s visibility and impact.
Basics of Color Wheel
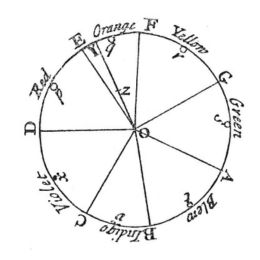
The color wheel, created by Isaac Newton in 1666, has familiar concepts such as primary, secondary, and tertiary colors, along with various hues, tints, shades, and tones for each category.
- Primary colors—red, yellow, and blue—are fundamental and cannot be produced by blending other colors. They serve as the foundation for creating all different hues.
- Secondary colors, which include green, purple, and orange, are formed by blending equal parts of two primary colors.
- Tertiary colors are derived by mixing a primary color with a secondary color, yielding six unique hues: blue-violet, blue-green, red-violet, red-orange, yellow-green, and yellow-orange.
Beyond these categories, an infinite array of colors can be achieved through shading, tinting, or toning a hue. A hue represents a pure pigment without adding any shade, tint, or tone, typically exhibiting a vibrant intensity. A shade is created by adding black to a hue, a tint by adding white, and a tone by adding gray.
Pastel and muted colors, often found in serene environments like yoga studios and spas, are known for their calming effects. Vibrant colors are joyful and energizing, while darker shades are linked to sadness and melancholy. Cool tones like blues and greens are associated with tranquility and relaxation, whereas warm tones with reds and oranges suggest energy and excitement. Each color carries associated emotions, both positive and negative. This comprehensive chart captures these associations and serves as a valuable reference tool.
Exploring Color Models
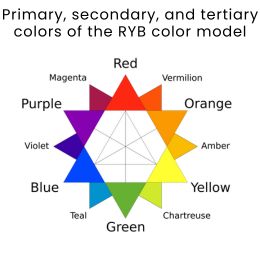
Image source
In the era of Isaac Newton and for many years following, the trio of primary colors—red, yellow, and blue—dominated the realm of color theory. However, the CMYK color model became vital with printing automation in the late 19th century. This model utilizes cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black) shades to achieve any desired color. Now, CMYK and its variants are fundamental for print media. The CMYK method employs a subtractive process, where mixing colors effectively reduces the light wavelengths reflected, ultimately crafting the final hue.
In this system, combining cyan, magenta, and yellow results in a dark, nearly black color; thus, the ‘K’ in CMYK stands for “key,” representing black.
Conversely, the RGB color model starts from complete darkness. It employs different intensities of red, green, and blue light to generate colors. Achieving maximum brightness in all three lights yields white. Established as a standard called sRGB in 1996 through a collaboration between HP and Microsoft, this model is crucial for digital displays and visualizes color overlap on screens. Unlike CMYK, RGB operates on an additive principle, where colors emerge by layering light, not pigment.
In practical applications, this means designers use RGB for all digital projects like websites, social media graphics, and more. Conversely, CMYK is essential for print materials. Designers typically begin projects in RGB and convert them to CMYK before printing to maintain color consistency across platforms. This process may require additional color adjustments to ensure uniformity across all used media.
Role of Different Colors in Business and Marketing

We often associate different colors with basic moods, emotions, and feelings. Color theories provide a structured approach to understanding color through a framework of definitions, concepts, and design applications. However, it’s important to note that the interpretation of each color can vary widely based on personal experiences and individual perspectives.
Acknowledging cultural variations that influence how colors are perceived in different contexts is crucial. For instance, while red may signify love and passion in Western cultures, it represents good fortune in Chinese traditions and mourning in South African societies. Here’s how brands can use different colors according to business branding and marketing:
- Red
Red is a vivid and compelling color, often linked to powerful emotions like passion, love, longing, energy, conflict, and danger. In advertising, red quickens heart rates and instills a sense of urgency, making it ideal for clearance sales and calls to action. It also stimulates the appetite, which explains its frequent use in restaurant logos. The vividness of red and its ability to stir potent emotions make it a top choice for brands aiming to capture attention and express excitement or urgency.
In the US, red frequently represents romance and can trigger various sensations (erotic feelings, peril, vigor, appetite). It is among the most emotionally charged colors and is known to elevate blood pressure.
- Pink
Pink represents joy, youthfulness, and femininity. It is commonly targeted at female audiences and can induce feelings of care, warmth, and sensitivity. Softer shades of pink lend a friendly, accessible vibe to a brand, while vibrant pinks express audacity and vigor.
Nevertheless, it’s crucial to employ pink carefully to sidestep associations with immaturity or frailty. Brands seeking a fun, feminine image often integrate pink into their palette.
- Purple
Purple has long been tied to royalty, aristocracy, and affluence, owing to purple dye’s historical scarcity and expense. It exudes sophistication, creativity, and a sense of exclusivity. Darker tones of purple suggest elegance and ambition, whereas lighter hues can introduce a playful or feminine flair.
In branding, purple is frequently chosen to denote luxury or high-end aspirations. However, its overuse can seem pretentious or overbearing, so it is usually used sparingly as an accent color.
- Blue
Blue is a highly adaptable choice in branding. It symbolizes trust, loyalty, and reliability. It’s the color of choice for banks and technology firms, reflecting professionalism and a sense of security.
Healthcare and wellness brands prefer soothing light blues for their calming effect, whereas bold, darker blues project authority and self-assurance. While blue can ooze a sense of calm and loyalty among customers, an excess can impart a sense of detachment or lack of warmth.
- Black
Black is synonymous with sophistication and elegance, embodying luxury and exclusivity. Premium brands, such as high-fashion houses and tech giants, favor it for its sleekness and formal aura.
In Western traditions, black also represents mourning and enigma, which enriches its branding utility with layers of depth and intrigue. Its authoritative vibe is prized in fashion and luxury markets, though when overdone, it can seem oppressive, prompting brands to blend it with other hues to maintain balance.
- Green
Green is the hue of nature, health, and rejuvenation, appealing to brands aiming for an eco-conscious or growth-oriented image. It radiates calmness and is tied to ideas of stability and endurance.
Fresh, light greens are linked to vitality and new starts, while rich, deep greens suggest sophistication and wealth. In marketing, green is employed to signal dependability and to create a peaceful, comforting environment, making it ideal for use in the health, environmental, and financial industries.
- Yellow
Yellow shines with optimism, vitality, and intellect. It’s an energizing color that both stimulates the mind and invigorates physically. In advertising, yellow captures attention and radiates cheer and hope. However, its overuse might induce anxiety, necessitating careful application. Brands like McDonald’s and Nikon use yellow to show a friendly, inviting atmosphere.
- Orange
Orange melds red’s vigor with yellow’s cheer, exuding enthusiasm, creativity, and warmth. It’s typically used to project a friendly, confident image, especially suitable for more casual, approachable brands.
Known for symbolizing affordability, orange is often seen in budget-conscious and value-driven businesses. Yet, it can also trigger irritation or seem juvenile if not used mindfully. Orange is particularly effective in attracting attention and prompting spontaneous purchases.
Tips for Making Effective Color Decisions in Business and Marketing

Choosing the right colors for your brand can be complex, as there are no straightforward rules. The most crucial factor is whether the color matches the essence of what you’re selling, known as “perceived appropriateness.” This means the color should fit your product and appeal to your target demographic.
Here are key considerations to guide your color selection process:
- Appropriateness for Your Brand: Research shows that the suitability of a color for a specific brand has a more significant impact on consumer response than the color itself. Therefore, assess whether the color aligns with what you are selling, perhaps by gathering customer feedback.
- Brand Personality Representation: Colors significantly influence brand perception and personality. Instead of adhering to typical color associations, choose colors that best represent the personality and attributes you want your brand to convey. Consider the traits you want your brand to reflect and select colors that embody these qualities.
- Audience Appeal: People’s color preferences can vary, often influenced by cultural perceptions and gender norms. Men generally prefer bolder colors, and women favor softer shades. However, challenging these stereotypes can benefit brands, offering a chance to stand out and appeal across traditional boundaries.
- Brand Differentiation: Selecting distinctive colors can help differentiate your brand from competitors. The Isolation Effect suggests that items that starkly contrast with their surroundings are more memorable. This principle can be applied by using a color scheme that includes base colors and contrasting accent colors, which can help highlight important elements and guide customer actions on your website.
- Color Naming: The names given to colors can also influence perceptions. Studies have shown that creatively named colors are more appealing than simpler ones. For example, “mocha” may be preferred over “brown.”
While the process can seem daunting, understanding these principles and considering your brand’s unique context will help you make more informed color choices that enhance your brand’s identity and appeal to your target audience.
Conclusion
Color theory is a powerful tool in business and marketing. It provides insight into how colors influence consumer behavior and brand perception. Understanding the emotional and psychological effects of colors allows brands to make strategic choices that resonate with their target audience.
By considering cultural variations and individual experiences, businesses can effectively use colors to evoke desired emotions, create strong brand identities, and differentiate themselves from competitors. Whether it’s the urgency of red, the reliability of blue, or the optimism of yellow, each color has unique properties that can enhance marketing efforts. These insights can lead to more effective branding and stronger connections with consumers.