How to Sell Courses Online: Monetize Your Knowledge
Posted: November 11, 2024 | Updated:
Selling online courses is a viable way for creators to earn money from their knowledge. If you’re considering creating your own courses, the process might be confusing due to mixed advice or concerns about failure.
Whether you’re a seasoned expert or someone eager to share what you know, there are numerous strategies for profiting from your expertise by developing an online course. This article will outline a clear, step-by-step method to sell courses online, drawing on established industry practices.
How Can Selling Online Courses Be a Profitable Source of Passive Income?
Selling online courses can be a profitable business. The global eLearning eCommerce market is expected to increase from $349.34 billion in 2024 to $2,285.67 billion by 2035, achieving a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.621%. This trend is driven by the rising demand for flexible, self-paced educational programs as more people look to learn new skills from home.
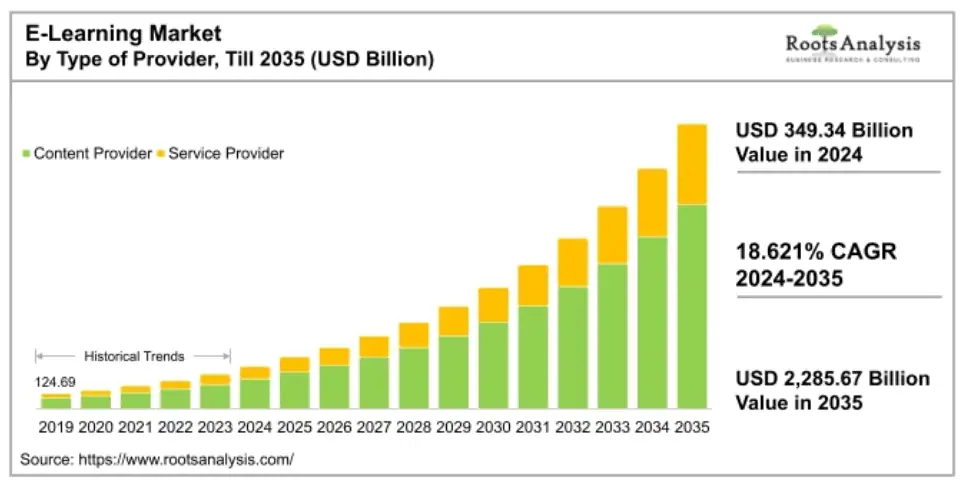
Source: Roots Analysis
Successful online course creators usually earn between $1,000 and $10,000 monthly, with top performers achieving up to six-figure incomes in under two years. An essential benefit of selling online courses is the potential for passive income. After a course is developed, it can generate income with little additional work, which is highly appealing to educators and entrepreneurs.
Nevertheless, success in this field depends on several factors, such as choosing the right niche, setting appropriate prices, and employing effective marketing strategies. Courses that cater to growing fields like technology and personal development draw more students, thus enhancing earning opportunities.

Image source
1. Finding the Niche for Your Course
The first obvious step before coming to the “selling point” is having the product in your hand! So, it’s essential to understand what you’re getting yourself into. Begin by pinpointing a particular topic or group you wish to concentrate on. This could be an area you are already skilled in or one where you aim to enhance your abilities before teaching others. Establishing a clear focus allows you to produce quality content and shape your brand around a specific niche.
While starting with a general topic and gradually refining your focus might seem more manageable, selecting a subject that addresses a genuine problem and has a significant market interest is essential. Determine why your course would appeal to potential learners.
Conduct online searches or consult your network to discover what people are interested in learning or what is trending within eLearning eCommerce. You should also analyze how other course creators handle similar subjects, including their pricing strategies and student enrollment numbers. Review their course outlines and spot areas where you can provide additional or unique content. This approach will help you define what makes your course distinct and valuable.

In 2025, online courses in various niches continue to perform well due to the increasing demand for skills and knowledge across multiple fields. Here are some of the top ideas:
- Tech and Programming: Courses on programming languages, especially Python and JavaScript, are consistently popular due to high demand in data science, web development, and automation. Cybersecurity courses also perform well, given the need for data protection skills as cybersecurity threats grow.
- Personal Finance and Investment: With a growing interest in financial independence and investment strategies, courses on budgeting, debt management, and stock market investing are widely sought after. Personal finance courses help individuals build long-term financial health, making this niche both profitable and sustainable.
- Digital Marketing: Topics such as SEO, social media marketing, and content creation are popular among professionals and entrepreneurs who want to improve their online presence. Digital marketing courses provide practical skills, making them highly attractive for small business owners and freelancers alike.
- Health and Wellness: Courses focusing on mental health, nutrition, and fitness have seen increased enrollment. Many people, driven by a heightened mental and physical health awareness, are interested in learning about stress management, mindful eating, and exercise programs.
- Language Learning: Language courses, especially English as a Second Language (ESL) and Spanish, are popular as globalization drives the need for multilingual skills in the workforce. This niche appeals to both personal and professional learners globally.
- Self-Development and Life Skills: Courses that help people with productivity, time management, and personal growth techniques are in high demand. These courses provide career and personal success tools, attracting learners looking for structured improvement strategies.
- Creative Arts and Photography: Creative courses, including photography, digital art, and videography, are popular among hobbyists and aspiring professionals. With the rise of platforms like Instagram and YouTube, more people want to develop skills to create visually appealing content.
2. Making a Course Plan
Creating an effective course outline is a critical step in organizing educational content that ensures comprehensive coverage of the subject matter and aligns with learning objectives. So, once you have identified your course category, Select the main topics and subtopics. Start by identifying the broad topics that will form the backbone of your course. Break these broad topics into subtopics, which should cover all necessary aspects of the main topic. This ensures a thorough exploration of the subject.
Arrange the topics and subtopics in a logical sequence. Topics should build upon each other, starting from basic concepts and progressing to more complex ones. This structure helps learners build their knowledge incrementally.
Establish clear learning objectives for every lesson or section. These objectives should articulate what learners are expected to understand or achieve after completing the lesson. Learning objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Specificity: Detail what students can accomplish or provide clear examples of applicable skills they will gain after completing the course.
- Measurability: Use quizzes, exams, and projects to assess and track student performance and progress throughout the course.
- Achievability: Set realistic goals considering the available resources and the student’s abilities. Ensure the course length is sufficient to meet its objectives and manageable for students. Research suggests that 5 to 10-hour courses are the most profitable, retaining around 75% profitability.
- Relevance: Ensure that the course objectives align with the broader goals of the curriculum.
- Timeliness: Define a clear timeframe for meeting the course goals. Choose the right course type based on your audience and course structure: short courses and masterclasses to gauge interest before launching a full-length course or membership sites to establish a sustainable business and cultivate a community.
Create a “Why” statement for each lesson that connects the learning objectives to real-world applications. This statement should justify why the lesson is important and how the knowledge can be used in practical scenarios. It helps learners see the value in the information being taught.
Pro tip: After you have designed your course, consider running a pilot session or seeking peer reviews. Feedback can provide insights into areas that may need further clarification or improvement. Use this feedback to refine your course content.
Here is a clear example of what an ideal outline should look like (we have taken an example of one of the top-selling courses in the US right now–Introduction to Programming):

Introduction to Programming
Objective: By the end of this course, students will gain a solid understanding of programming fundamentals, learn multiple programming languages, and be able to create their own simple applications.
Module 1: Understanding Programming Basics
- Lesson 1: Introduction to Programming
- Lesson 2: Understanding Programming Languages
- Lesson 3: Setting Up Your Development Environment and Writing Your First Program
Module 2: Introduction to Web Development
- Lesson 1: Basics of HTML and CSS
- Lesson 2: Introduction to JavaScript
- Lesson 3: Building a Simple Web Page
- Lesson 4: Styling with CSS
Module 3: Exploring Python
- Lesson 1: Python Basics
- Lesson 2: Working with Data in Python
- Lesson 3: Introduction to Libraries: NumPy and Pandas
- Lesson 4: Building Simple Applications with Python
Module 4: Java Fundamentals
- Lesson 1: Java Programming Essentials
- Lesson 2: Object-Oriented Programming in Java
- Lesson 3: Handling Exceptions and Debugging
- Lesson 4: Java in Web Applications
Module 5: Databases and SQL
- Lesson 1: Introduction to Databases
- Lesson 2: Basics of SQL
- Lesson 3: Integrating SQL with Programming Languages
- Lesson 4: Working with NoSQL Databases
Module 6: Introduction to Mobile App Development
- Lesson 1: Mobile App Development for Android
- Lesson 2: Mobile App Development for iOS
- Lesson 3: Cross-Platform Development Basics
Bonus Module: Advanced Programming Topics
- Lesson 1: Introduction to APIs
- Lesson 2: Basic Security in Programming
- Lesson 3: Data Structures and Algorithms
Next Steps
- Recap and Review
- Planning Your Programming Career
- Continuing Education and Resources
Once your outline is set, start developing the course materials. These can include lecture notes, PowerPoint slides, reading assignments, and multimedia resources.
Ensure these materials align with your learning objectives and are engaging for learners. This leads us to the next point.
3. Creating the Content
With a clear understanding of your course’s central topic and a detailed roadmap ready, it’s time to move into the creation phase.
As an expert and content creator, you’re already equipped to craft educational materials tailored to your audience. D diversifying your teaching methods to address various learning preferences requires integrating video lectures, text-based lessons, quizzes, and hands-on exercises.
Creating effective course content involves organizing information into clear, manageable learning modules and presenting it engagingly, simplifying complex subjects for learners.
Developing course materials for your online program may seem daunting, but it can be straightforward. Begin by repurposing existing materials like blog posts, articles, or YouTube videos into course content. Alternatively, you could draw inspiration from popular content within your niche or utilize podcasts, webinars, and interviews with industry experts to generate fresh content ideas.
Based on your earlier planning, select a content delivery format- videos, PDFs, or audio recordings—that best suits your educational goals and enhances clarity for your students. Mixing various formats can boost engagement and improve learning outcomes. Keep lessons concise for easy consumption; aim to keep video lessons under 50 minutes, and don’t cut them too small as they may seem to lack depth or be too vague. Additionally, include case studies and practical examples to increase the relevance and applicability of your content.
Pro Tip: Quality is sometimes more important when selecting the course, so prioritize high-quality video production. Investing in professional lighting and audio equipment can significantly enhance the appearance of your video lessons. Charts, infographics, and animations can help clarify complex concepts. Screen captures that illustrate processes step-by-step can be very effective for technical subjects. This approach ensures that the content is both explicit and visually engaging.
Creating Effective Course Titles to Attract Students and Boost Enrollments
A strong course title is essential for attracting students and driving enrollments. A well-designed title doesn’t just describe the course; it appeals to the audience and conveys its purpose.
- Keep It Clear and Concise
Your course title should reflect the subject matter in simple, direct language. Avoid complex terms that could deter potential students. Aim for a title under 50 characters to ensure readability.
- Be Specific and Outcome-Focused
A targeted title speaks to your audience more effectively than a generic one. Include the niche and key outcomes. For instance, a title like “Personal Finance and Investment: Master Budgeting and Build Your Wealth” is more compelling than “Learn Personal Finance.” This approach clarifies the course scope and expected results.
- Use Relevant Keywords
Utilize tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Google Keyword Planner to find popular search terms related to your topic. Including relevant keywords in your title can boost search engine rankings, making your course easier to find.
You can conduct A/B tests by developing several landing pages, each featuring a different title, to determine which one performs better.
- Add Words that Highlight the Value
Use words that emphasize the course’s benefits, like “transform,” “effective,” or “proven.” These terms can make your title more engaging and motivate potential students to explore further.
4. Choose the Right Platform to Sell
Various platforms and tools are available to host and sell courses online. Selecting the appropriate venue for sales is crucial to making your online course business successful.
Choosing the right platform helps guarantee that students can access your content efficiently and reliably, making it easy for them to view your lessons. Using a platform designed for online courses can also enhance engagement and improve outcomes by offering an interface focused on good user experience. Here are some options:
1. Online Learning Marketplaces
Platforms such as Udemy, Mighty Networks, Skillshare, and LinkedIn Learning allow educators to reach large audiences without the need to build personal websites or engage in heavy marketing. An online course marketplace manages essential aspects like hosting, payment processing, and student recruitment, making it a practical choice for instructors who prefer to concentrate on creating content.
With their substantial active learner bases, these sites provide new instructors immediate access to numerous potential students. This setup helps educators expand their teaching reach with low initial costs, particularly beneficial for newcomers or those without a built customer base.
Despite offering significant visibility and easier access, these platforms do require compromises. Instructors often relinquish a portion of their earnings and have limited influence over course pricing, as these platforms may offer promotional discounts. High competition on these sites can also challenge new courses to gain visibility without distinct marketing strategies or unique course offerings.
Nevertheless, an online courses marketplace is a valuable entry point for many educators. It combines exposure and operational support to help them develop their presence and explore online teaching opportunities.
2. Self-hosted Online Course Website
Creating a self-hosted online course website allows educators complete control over their content, pricing, and the student experience. Unlike third-party platforms, hosting courses on your website lets creators keep a larger portion of the revenue, avoiding platform fees or revenue sharing. This method allows instructors to design, structure, and deliver their courses, providing a user experience that aligns with their brand and teaching approach. This option is ideal for those focused on long-term brand growth and profit maximization.
Self-hosted websites also provide flexibility in pricing, course format, and marketing strategies. Educators can develop courses of varying lengths, include diverse content types, and set their own prices without the constraints of an external platform. However, owning and operating a self-hosted site comes with additional responsibilities and some upfront costs.
Instructors must manage expenses like domain registration, hosting, and web design services. Marketing efforts can also be more demanding, as self-hosted sites lack the automatic audience on platforms such as Skillshare or Udemy.
Many turn to content management systems like WordPress, which supports course management and student tracking, with plugins like LearnDash or Teachable to manage their sites more effectively. Website builders like Wix provide easy-to-use interfaces for those who prefer not to code, although they may offer less customization than WordPress or other CMS platforms.
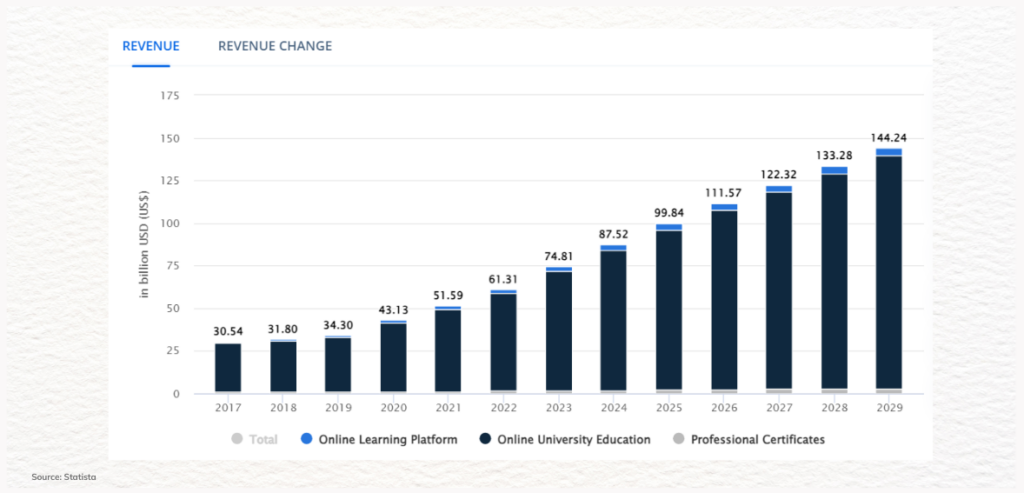
3. Online Course Platforms
Online course platforms are tailored to assist educators and course creators establish and expand their online course offerings. These platforms supply a range of tools and functionalities that aid in course development, marketing, and sales.
- Thinkific: This platform is a top choice for those seeking flexibility and ease of use. It offers a variety of customizable course creation tools, student engagement options, and diverse pricing plans, including a comprehensive free tier. Thinkific is favored for its powerful course builder, no transaction fees on paid plans, and support for multimedia lessons, quizzes, and certificates, which enhance the learning experience.
- Teachable: Renowned for its simple course-building tools and strong content engagement capabilities, Teachable enables creators to sell courses online on customizable pages and features integrated payment processing. The platform has a variable fee structure depending on the chosen plan and includes features to enhance monetization strategies, though its email marketing tools could see improvements.
- Kajabi: As an all-encompassing platform, Kajabi suits creators seeking advanced marketing tools, such as email automation, sales funnels, and membership site management. Although it is pricier than other platforms, Kajabi’s robust marketing and customer relationship tools make it a solid option for those aiming to grow their course business significantly.
- Podia: Ideal for creators looking to market online courses, digital products, and memberships together, Podia features an easy-to-use interface with a broad selection of content delivery tools. It does not offer a free plan, but its pricing is competitive for the features provided, which include email marketing and the option for custom domains, appealing to budget-conscious creators.
- LearnWorlds: Optimized for those planning to offer interactive video courses and mobile applications, LearnWorlds excels with its white-label capabilities and powerful analytics. The platform is particularly effective for larger audience engagement or creators focused on a more dynamic and interactive learning environment.
5. Price Your Course Right
When setting a price for your online course, it’s important to balance your potential revenue with the value offered to your audience. Start by evaluating the costs associated with creating the course content. This includes the time and resources spent developing materials such as scripts, videos, and graphics. You must also consider the expenses for software and hosting services that support content management and delivery.
Additionally, factor in the costs for marketing and advertising, which might include email marketing services, social media ads, and search engine optimization (SEO) efforts. Don’t forget about the payment processing fees charged by gateways handling your transactions, taxes, and other business-related fees that vary by location and business structure.
An effective way to determine a suitable price is to use an online course pricing calculator. To suggest an optimal price point, these tools consider various factors, including your revenue goals, audience size, conversion rates, development costs, desired payback period, and competitor pricing.
6. Boost Course Value and Maximize Revenue
Enhancing the value of your online course can allow you to raise its price and attract more students. To do this, you could offer bonus materials. For example, you can collaborate with industry experts to include guest lectures or specialized content, create additional resources like reports, case studies, templates, or supplementary lessons, and implement referral incentives that reward current students for bringing in new enrollees.
These strategies broaden the appeal of your course and foster a sense of community among your students. Assigning a monetary value to these bonuses can also increase the perceived worth of your course.
Another effective approach is introducing upsells during the purchase process, which boosts revenue. You could also offer personalized coaching, including one-on-one sessions, monthly webinars, email consultations, or even in-person meetings.
Additionally, organizing live group training sessions can provide more in-depth discussions on advanced topics, which adds significant value for students seeking a more engaged learning experience. It’s important that these upsells are relevant to your course content and cater to the specific needs of your target audience.
7. Promoting Your Courses
After determining your course pricing, the next step is effectively advertising your course. Effective marketing is crucial for reaching your intended audience and meeting your sales goals. Various strategies are available, and finding the most effective method for attracting potential students may require trial and error.
Numerous proven tactics can enhance the visibility of your course and increase sales. Experiment with different techniques to identify those that yield the most favorable return on investment (ROI).
- Sales Funnel
To effectively sell courses online, a structured sales funnel is necessary to lead potential students from showing initial interest to making a purchase. This funnel consists of sequential steps designed to increase awareness of your course among potential buyers and motivate them to sign up.
The first step involves creating awareness through various marketing channels such as social media, email campaigns, or online advertisements. Once potential learners know about the course, the next step is to generate interest by highlighting the course content and its advantages. Once interest is established, motivate these potential students to take action, such as registering for the course. Following course completion, encourage them to leave a review or consider other courses you offer.
- Lead Magnets
Lead magnets offer free resources in exchange for contact details, which helps build an email list and attract new students. These resources might include eBooks, checklists, or free templates.
For instance, if your course teaches web development, you could offer a free “Intro to HTML” checklist to draw in learners interested in this area. This offers them immediate value and piques their interest in your full course offering. Lead magnets are also effective in affiliate marketing, where other businesses promote your course and gain access to your lead magnets to offer their audiences.
- Sales Page
A well-crafted course sales page is crucial for turning visitors into enrolled students. It should encompass all the details a prospective student requires to decide whether to enroll. Essential components of this page include a banner that prominently features the course name, a catchy tagline, and a clear call-to-action (CTA) to prompt immediate responses.
The course description should clearly articulate what the course entails and provide an overview of the curriculum to give prospects an insight into what the course offers. Including an instructor bio with relevant background and credentials can help establish credibility, while adding elements like testimonials, FAQs, or a money-back guarantee can enhance trust and encourage enrollments.
- SEO
Enhancing your course website for search engines is vital to making it more discoverable. Simple measures such as incorporating relevant keywords throughout your site in titles, descriptions, and course content can significantly boost its visibility.
With most web traffic coming from mobile devices, ensuring your website is mobile-friendly is essential. Additionally, producing high-quality, relevant content, such as blog posts or videos that align with your course theme, can enhance your SEO efforts. Combining these optimization strategies with consistent content can lead to long-term success.
- Content Marketing
Content marketing focuses on generating valuable content to draw in potential students. Starting a blog related to your course subject can be a strategic way to offer helpful information that guides readers toward your course. For instance, if your course is on digital marketing, blogging about fundamental SEO techniques or content strategy tips can lead readers to explore your full course offerings.
Sharing this content on social media platforms can expand your reach, although it’s important to note that building visibility and achieving measurable outcomes from content marketing typically requires patience.
- Paid Advertising
Paid advertising can be an effective and quick way to drive traffic to your course. Options include search engine ads, where you use specific keywords to appear in search results and social media ads on platforms like Facebook and Instagram that allow for targeted campaigns for your ideal audience.
Display ads, such as banners and pop-ups, can be placed on relevant websites, while native ads are designed to blend naturally into a page’s content, encouraging interaction. These customizable ads can be optimized to reach particular audiences, helping attract students who are most likely to be interested in your course.
- Email Marketing
Email marketing is also highly effective for staying connected with your audience and promoting your courses. Building a list of subscribers who have shown interest in your topics gives you a direct line of communication. Personalization techniques, such as tailored subject lines and content, can make your emails more engaging.
Segmentation is also helpful, allowing you to group subscribers based on interests or past enrollments to send more relevant information. A/B testing can be used to experiment with different subject lines and designs to determine what resonates best, and tracking metrics like open rates, click-throughs, and conversions enables continuous improvement. This approach to email marketing allows you to keep potential students informed about new courses and maintain a loyal student base.
- Social Media
Utilize short-form content on social media platforms such as TikTok, Snapchat, and Instagram, which are popular for their brief video formats. If your course is newly launched, consider collaborating with a well-established social media account to promote your course jointly.
Alternatively, you could set up a dedicated account to post short videos highlighting the key aspects of your course content.
8. Continuously Enhance and Optimize Your Online Course
Once your course goes live and you welcome your initial cohort of learners, monitoring their interaction with the material is critical. Pay close attention to metrics such as video engagement rates, quiz participation, and course completion figures to gain insights into student experiences. Use this information to pinpoint areas needing refinement, which might include:
- Course Structure: Reassess the sequence of lessons and the duration of modules to ensure a smooth educational progression.
- Content Quality: Revise or improve content with high dropout rates or multiple student replays.
- Interactivity: Boost student involvement by incorporating more quizzes, practical exercises, or discussion opportunities.
Leverage these insights to test changes in course design, content delivery, and pricing models. Your goal should be to improve the course’s value and impact, making it more appealing to students and meeting their educational requirements more effectively. This improvement will draw in more learners and help you lay a strong foundation for future offerings by creating a track record of quality and consistent enhancement.
Conclusion
Creating and selling online courses offers a dynamic avenue for monetizing your expertise and achieving sustainable income within the eLearning eCommerce market. You can attract a dedicated audience by meticulously selecting your course niche, crafting a comprehensive course plan, and employing strategic marketing tactics. Your success hinges on your ability to produce high-quality, engaging content that meets the evolving needs of learners.
By continuously analyzing performance data and making informed adjustments, you can enhance your course’s effectiveness and increase its reach. Embrace this opportunity to impart knowledge and foster skill development, and watch as your online education venture flourishes, creating impactful learning experiences that resonate with students worldwide.


