Payment Solutions for the Gig Economy: Addressing the Needs of Freelancers and Contractors
Posted: October 08, 2024 | Updated:
The gig economy has grown substantially, with an estimated 76.4 million freelancers in the United States as of 2024. This number represents a consistent annual increase of at least 2 million freelancers since 2017 and is projected to surpass 90 million by 2028.
The flexibility of the gig economy provides significant advantages for freelancers, particularly the ability to achieve financial stability on their terms. This self-directed work model is also beneficial for companies. Hiring freelancers allows businesses to adjust their workforce size as necessary, reduce costs by avoiding permanent employment expenses, and access a vast talent pool.
However, gig economy payment processing to freelancers can be problematic. Traditional methods like checks or money orders are often too slow, and cash payments are impractical for long-distance arrangements. Thankfully, more efficient payment solutions are available. Continue reading to discover effective methods for compensating freelancers promptly and securely.
What Is a Gig Economy?

The gig economy is a labor market sector characterized by short-term, flexible jobs, often coordinated through digital platforms like apps or websites. Workers in this economy are independent contractors, not permanent employees, and are paid per task instead of a regular salary. This structure provides flexibility in work hours but typically lacks employee benefits such as health insurance or paid leave.
Jobs within the gig economy include various services such as ride-sharing (Uber, Lyft), food delivery (DoorDash, UberEats), and freelance roles in writing, design, and software development. It also encompasses asset-sharing services like property rentals through Airbnb. Digital platforms have significantly contributed to the growth of this sector by simplifying the process of connecting freelancers with short-term jobs or clients.
Many individuals are drawn to the gig economy for the flexibility it offers in scheduling and the potential to work from different locations, including remotely. For some, it serves as an additional source of income, while for others, it is their main financial support.
The Rise of the Gig Economy
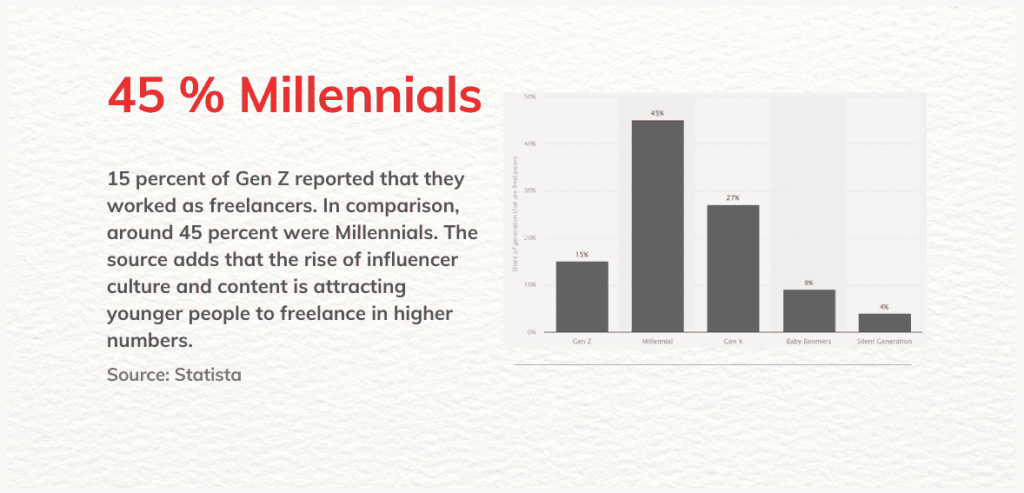
Source: Statista
The gig economy has expanded significantly over the last ten years, influenced by various economic, technological, and social factors. This growth is primarily fueled by the widespread availability of digital platforms like Uber, Fiverr, and Upwork, which link gig workers with potential clients. Technological advances, particularly in remote collaboration tools, have simplified the process for individuals to freelance or pursue side jobs from almost any location.
Economic factors also play a crucial role in this growth. The flexibility of gig work attracts many, especially younger individuals and immigrants, who view it as an opportunity for financial independence. For some, gig jobs supplement their primary income; for others, they become a main source of earnings due to economic needs. The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact, forcing many into freelancing as they lost traditional jobs, and rising inflation has driven more people to seek gig work for extra income.

Source: Statista
Companies see the advantage of hiring independent contractors to tap into specialized skills without the commitment of full-time hires. This strategy helps businesses control costs and adjust their workforce size as necessary.
The Challenges with Paying Gig Workers
Several gig economy payments-related obstacles can affect their cash flow and overall business operations. Common issues include:
- Delayed or Inconsistent Payments:
Freelancers frequently face delays in receiving payments from clients. This can be especially problematic when payments are made via checks or other slower methods like mailed invoices, which can take weeks to process.
Freelancers who rely on regular payments for their living expenses or business costs may experience financial strain when payments are delayed by 30, 60, or even 90 days. While setting clear payment terms and sending reminders can help, freelancers often have limited control over when clients actually pay their invoices.
- Costly International Transactions:
Freelancers working with clients in other countries often face high fees for international payments. Banks and transfer services charge varying fees for international wire transfers, which can be substantial. For instance, U.S. banks such as Fifth Third Bank charge up to $85 for outgoing transfers, and others like Wells Fargo and Bank of America charge between $40 and $65.
Additionally, freelancers may incur intermediary bank fees, currency conversion costs (typically between 4% and 8%), and taxes, which all reduce their earnings. These costs make cross-border work more expensive and challenging to manage financially.

- Currency Conversion Fluctuations:
Freelancers paid in foreign currencies can see their earnings decrease due to fluctuations in exchange rates. The freelancer may receive less than expected if a currency weakens after a payment agreement.
Some banks and payment platforms offer automatic currency conversions, but their rates are often less competitive, further reducing the freelancer’s income. Using specialized platforms like Payoneer can sometimes provide more favorable exchange rates and quicker transactions.
- Tax Management and Record Keeping:
Handling taxes is another challenge, especially for freelancers with international clients or multiple revenue streams. U.S. freelancers, in particular, must navigate forms like the 1099-K and W-8BEN-E, depending on their residency and income sources.
Accurate record-keeping, understanding tax deductions, and complying with regulations add complexity to their workload. Many freelancers outsource tax preparation or rely on accounting software to track earnings and ensure proper tax filing.
How Modern Payment Innovations Are Shaping the Future of the Gig Economy?

Modern payment innovations have significantly transformed the gig economy by enhancing the efficiency, flexibility, and security with which freelancers and gig workers manage their finances. These innovations’ solutions stand out as pivotal elements driving this change. They offer faster, more accessible solutions than traditional payment methods like cash or checks.
- Digital wallets, including popular platforms like PayPal, Venmo, and Cash App, have become vital for gig workers to manage and receive payments securely and conveniently via smartphones. The ease of use provided by these platforms has led to their widespread adoption. The mobile payment market is projected to grow to $12.06 trillion by 2027, reflecting an increasing consumer preference for cashless transactions. This growth is particularly relevant in the gig economy, where workers depend on swift and efficient payment methods.
- Cross-border payment solutions effectively tackle the complexities of international transactions within the gig economy. Notable companies such as TransferWise, Payoneer, and Revolut provide freelancers with multi-currency accounts, enabling receipt of payments in various currencies while minimizing conversion costs. These platforms also offer competitive exchange rates and quicker transaction settlements, thus improving the overall efficiency of international payments.
- Instant payout solutions like those provided by Stripe or Square enable workers to access their earnings immediately, enhancing liquidity and reducing dependence on traditional bank processing times. In 2022, there was a 41% increase in global real-time payments, underscoring a shift toward immediate fund access. This capability is especially beneficial for gig workers who frequently experience unpredictable cash flows.
- For gig workers who operate in physical settings, mobile point-of-sale (mPOS) systems deliver a practical solution for processing payments anywhere. Services like Shopify POS, Square, and SumUp equip freelancers with compact, portable card readers that pair with smartphones or tablets, allowing them to process credit and debit card payments on-site. This adaptability is especially valuable for retail, food service, and event professionals, facilitating seamless financial transactions in mobile environments.
- Furthermore, cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum are gaining traction as payment options, especially among gig workers engaged in international markets. These digital currencies facilitate decentralized, low-fee, and borderless transactions, appealing to international freelancers seeking financial autonomy. With the global blockchain market anticipated to reach $39.7 billion by 2025, cryptocurrencies are expected to play an increasingly prominent role in the payment landscape.
- Freelance management platforms combine payment processing with comprehensive project management tools to streamline the entire workflow for freelancers. Platforms such as Upwork, Freelancer.com, and Fiverr facilitate employer funding of escrow accounts, enable secure payment releases upon project completion, and allow efficient invoice tracking. These freelance payment systems also manage tax withholdings and compliance, significantly reducing the administrative load on freelancers and enhancing their focus on project execution.
Top Payment Solutions for Freelancers and Contractors
Here are various payment methods for freelancers, focusing on their transaction fees and suitability based on ease of use:
1. PayPal
Fee: 2.9% + $0.30 per transaction; up to 4.4% for international transfers.
Effective for rapid, reliable payments on a global scale. PayPal facilitates instant payouts, though these come with fees, and is widely recognized in many countries. The main drawback is the elevated fees for international transactions.
2. Payoneer
Fee: Ranges from 0% to 3%, plus 2% for conversions to foreign currencies.
Payoneer is a viable option for low-cost international payments. It supports local bank accounts in various currencies, making it beneficial for freelancers dealing with clients abroad and a solid alternative for PayPal for substantial international transactions.
3. Skrill
Fee: 3.99% for currency exchanges.
Skrill is suitable for low-expense transactions and secure payments. It is useful for freelancers requiring quick payment processes and those who operate internationally, although it imposes certain limits on high withdrawal amounts.
4. Escrow
Fee: 6.5% of the transaction value.
Escrow is ideal for larger payments that need secure handling. It secures funds until project completion, adding a layer of protection for all involved parties. Escrow is particularly useful for sizable projects where mutual trust is crucial.
5. Wire Transfer
Fee: Varies from $0 to $50, based on the banks and geographical regions involved.
Traditional yet less common. Wire transfers are reliable and suitable for large transactions, especially international ones, but tend to be slower and may incur higher fees compared to other methods.
6. Debit/Credit Card
Fee: Typically between 3% and 5%.
It is ideal for quick, direct payments and is widely used on Upwork, Freelancer, and Fiverr platforms. While suitable for international transactions, they might attract higher fees.
Strategies for Reliable Payment as a Freelancer
For freelancers, consistent and prompt payment can be a challenge, but implementing certain strategies can increase your chances of getting paid on time:
- Implement a Time Tracker: Utilize a time tracker, such as Apploye, to keep accurate records, especially for projects billed by the hour. This ensures you can bill clients accurately and transparently. Time trackers like Clockify or Toggl also let you generate reports and invoices directly from the hours logged, simplifying the process of demonstrating your work to clients and facilitating payment.
- Always Use a Contract: A contract is crucial for establishing clear client expectations. It should detail payment terms, project scope, and deadlines. A contract legally commits clients to the agreed terms, which helps reduce the risk of delayed payments or disputes.
- Opt for Simple Payment Methods: Choose widely recognized and easy-to-use payment methods, such as PayPal, Stripe, or bank transfers. Digital wallets like Google Pay and Venmo provide easy payment solutions for clients worldwide. Using well-known, straightforward payment platforms helps minimize complications and encourages clients to pay quickly.
- Use Professional Invoice Software: Employing professional invoicing tools like Invoicely or Invoice Fly helps make the payment process more efficient. These platforms often feature the option to add payment links directly in the invoices, facilitating immediate payment with just a click. Making it easy for clients to pay increases the likelihood of swift payments.
Conclusion
The gig economy continues to grow, driven by its flexibility and the demand for specialized, on-demand services. However, the challenges freelancers and contractors face, particularly around timely and efficient payments, remain significant. Addressing these challenges requires adopting modern payment solutions catering to gig workers’ unique needs.
Digital wallets, cross-border payment platforms, instant payment services, and freelance management tools offer promising ways to enhance payment efficiency and security. By leveraging these innovations, freelancers can maintain better control over their earnings, reduce financial uncertainties, and thrive in the evolving gig economy.


